
The following factors may contribute to the development of knee joint pain:
- Excessive physical activity that does not meet the age requirements, leading to joint damage.
- sedentary life?
- suffered injuries in the area of the knee joints - knee dislocations, fractures, ruptures and ruptures of the ligaments, damage to the meniscus body, severe falls on the knee, bruises.
- increased body mass index, which causes increased pressure on the joints, meniscus rupture.
- heredity;
- arthritis or other diseases of the joints (inflammation can lead to swelling or the accumulation of a large amount of synovial fluid in the joints, causing the destruction of cartilage tissue).
- metabolic disorders that lead to the excretion of calcium by the body.
- diabetes mellitus of any type, hormonal disorders and other pathologies of the endocrine system.
- chronic or older diseases of inflammatory and infectious nature.
- violation of blood flow;
- lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid, gout and psoriatic pathologies, ankylosing spondylitis.
- flatfoot, due to which the center of gravity shifts and the load on the joint increases.
- nervous overload and stressful situations.
Why Knee Joint Arthropathy Occurs
Most of the time, people themselves become the culprits of the development of such an intractable disease. Often, when pain occurs in the knee joint, people ignore the painful sensations, preferring to go to the doctor to use any medications that simply mask the pain.
After a few years, you still need to consult a specialist, as with such a diagnosis, self-medication will not work. However, the severity of the arthropathy will be at least moderate. Ointments, intra-articular administration of hyaluronic acid and preventive physical treatment are no longer enough here, as could be done in the early stages of the disease. Most likely, you will need to act radically, including sometimes using surgery.
Symptoms and diagnosis of knee joints
The disease can be distinguished by the following characteristics:
- Pain syndrome. Painful sensations usually appear suddenly, but most of the time with physical exertion, albeit mild. The pain can be of a different nature. At first, these will be weak lumbar (unfortunately, few people pay attention to them). Mild pain that occurs only periodically can last for months or even years, until the disease progresses to a more serious stage.
- Significant knee deformity. A similar symptom is characteristic of the later stages. And at the beginning of the development of arthropathy, the knee swells and swells a little.
- The appearance of dense formations on the back wall of the knee joints. The accumulation of a large amount of synovial fluid in the cavity of the Baker bladder or in the joint itself.
- A sharp crease of the joints, which is accompanied by pain.
- Reduced joint mobility. This is especially pronounced in the later stages of the joint. In this case the bending and extension of the knee causes intense pain and in the last stages the movement becomes almost impossible.
REPORT! In a patient with arthritis, gait changes: it is characterized by drooping legs and lameness.
Pathogenesis of knee joints
Experts distinguish between primary and secondary arthropathy.
Primary arthropathy of the knee joints
For primary gonorrhea, the following processes are typical:
- The articular cartilage is capable of constantly deteriorating and at the same time being renewed quickly. Under normal circumstances, these two processes should balance each other. With age, cartilage destruction occurs at the same rate, but its recovery slows down. The mass of an individual plays an important role here. Indeed, if the mass of a person is 70 kg, then in 10 steps on one leg will carry 700 kg and the one who weighs 120 kg will carry up to 1200 kg, which will become a significant load on the joints and cartilage, which will wear out. faster because of this.
- It is important to remember: the joint is supplied with useful information only when it moves. A sedentary lifestyle leads to a slowing down of metabolic processes, which is why the necessary nutrients do not reach their destination.
- The likelihood of developing knee arthritis increases in people whose parents have suffered from this disease.
Secondary arthropathy of the knee joint
It is developed for the following reasons:
- Multiple injuries. In a person of any age, they will cause excessive pressure on the cartilage. When any bone covered by cartilage breaks, abnormalities appear, the so-called "steps". In this area, now, with any movement, the joint will wear out, leading to joints.
- Development of rheumatoid arthritis, Koenig's disease, appearance of purulent inflammation in the joint area.
- Vascular dysfunction.
Classification and developmental stages of knee joint arthropathy
Orthopedists divide the gonorrhea into stages, on which further treatment of the disease depends. Of course, the course of treatment will depend on other factors, for example, the reasons for the development, location and nature of the arthropathy.
GREAT! Quality treatment can be prescribed only by a doctor after a complete study of the picture of the disease. Self-administered therapy can only worsen the state of health.
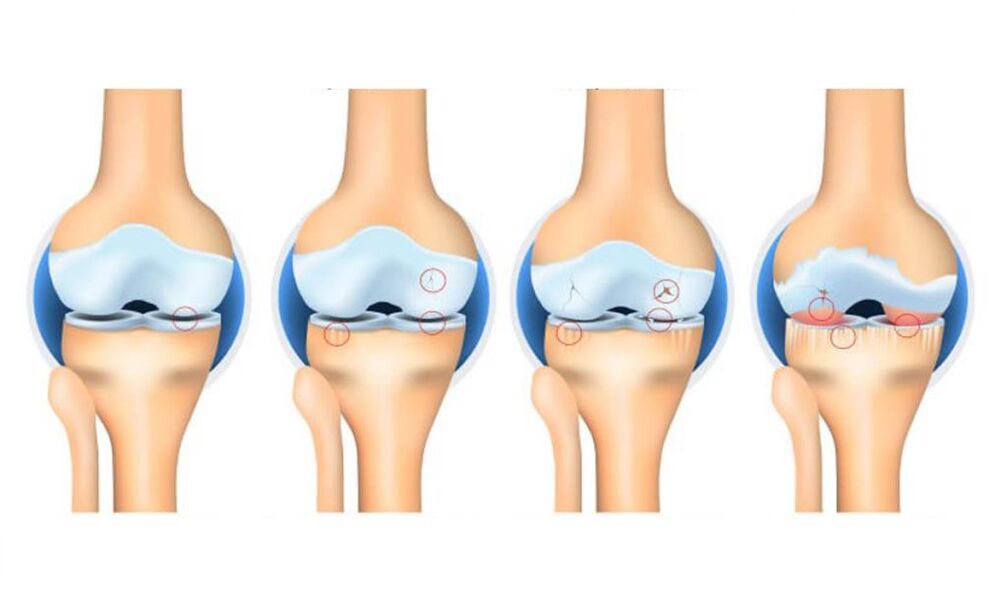
The main classification divides the gonorrhea into four stages of development:
- Primary stage. At this stage, the disease is just beginning. The external symptoms are minimal or completely absent, the shape of the joint is in satisfactory condition. Symptoms include only mild discomfort or heaviness in the knee after long walks, as well as intense physical exertion. An x-ray will be minimal information: an x-ray can only show a slight narrowing of the joint space. Unfortunately, at this stage, a person does not seek medical help because of the insignificance of the symptoms.
- The second stage is characterized by a noticeable pain syndrome, especially when walking and climbing stairs, as well as at night. The severity of the pain decreases at rest. The movement of the joint becomes difficult. There is a squeaking or creaking of the knees while walking. The radiograph shows the narrowing of the joint space as well as the osteophytes. The patient begins to limp.
- When the arthropathy has passed to the third stage, the pain syndrome will be constantly felt, even if there is no movement. The processes of deformation and degeneration pass into an irreversible stage. The deformation of the joint becomes intense, the distance between the articular surfaces decreases significantly, many osteophytes increase in size. Painful sensations now bother the patient even in a state of complete rest. A person depends on external support (walkers, sticks) and needs help from other people. Conservative treatment at this stage is less effective.
- The fourth stage is characterized by constant debilitating pain. Osteophytic growths increase in number and size, cartilage is completely destroyed, joint space is sparsely located or completely absent, bones are severely deformed. Even weak movements become torture for the patient. At this stage of the knee joint, the patient is recognized as disabled. In the absence of surgery, the disease can lead to disability.
Joint complications of the knee joints
Advanced arthropathy can lead to dislocations and dislocations of the knee joint. With dislocation, the epiphysis of the femur extends completely out of the joint, making movement in the joint impossible and the axis of the foot virtually shifting to the side. Fortunately, such a negative variant of disease development is rather rare.
Dislocations are more common. They are characterized by a partial displacement of the joints between them and a slight deviation of the tibia axis. In this case, the subluxations are accompanied by severe pain and dysfunction of the joints.
Neglect of the disease can lead to complete loss of lower limb function.
CAUTION! The habit of rescuing a aching leg sometimes causes deformity of the intervertebral discs and the appearance of hernias.
Consequences of neglected knee joint
The advanced stage of knee joint is almost always characterized by the following adverse symptoms:
- pain around the clock, from which no analgesic can save.
- loss of support for one limb (it is impossible to stand on a sore leg or at least touch it).
- immobilization of the articular block.
- strong curvature of the bones around the knee.
- intense swelling around the affected area.
Methods for treating knee joint arthritis
Prescription treatment depends on the degree of development of the disease. There are many treatment options.
hormones
These drugs are prescribed for severe flare-ups, accompanied by arthritis and severe pain. Hormones are usually injected. The following drugs are most commonly used:
- Fosterone?
- Diprosfan;
- Hydrocortisone.
The course of hormone therapy is usually short; injections are given only during a period of severe exacerbation. Hormones are administered at an average frequency once every 10 days.
Chondroprotective
Chondroprotectants are prescribed in the early stages of the disease. This treatment is currently considered the most effective and safe: there are practically no contraindications and side effects occur in the rarest cases.
The drugs aim to repair cartilage, improve metabolic processes, nourish cartilage tissue and protect it from further destruction. But in the later stages of the joint, the chondroprotectors are also powerless.
This group of drugs is produced in the form of injections, ointments, gels, tablets.
Vasodilators
These funds are necessary to eliminate spasm of small blood vessels, increase blood circulation and provide nutrients to the affected joint area. It is prescribed for taking vasodilators together with chondroprotectants.
If synovial fluid does not accumulate during the knee joint (there is no arthritis), the use of heating ointments is recommended.
Hyaluronic Acid
Alternatively, this tool is called intra-articular fluid addition, as the composition of the acid is similar in composition to intra-articular fluid. When acid is injected into the joint, it forms a membrane that prevents strong cartilage friction during movement, affects the extracellular matrix, improves metabolic processes in the joint and also activates the production of its own hyaluronic acid in the joint - i. e. restores functionof the joint to normal, stopping the pathological processes that destroy the cartilage. . . .
Acid treatment is prescribed only when the flare-up of arthritis is eliminated.
Physiotherapy
A course of physiotherapy exercises will bring positive results only if it is prescribed by a doctor after a complete study of the medical history and all the exercises are performed under the supervision of a specialist.
Self-medication often leads to worsening of the condition of the joints. Exercise therapy is prescribed for the following purposes:
- slowing the development of stiffness.
- prevention of further destruction of cartilage tissue.
- elimination of muscle spasm, leading to pain.
Physiotherapy
As an additional treatment, various procedures can be prescribed: electrophoresis, acupuncture, laser treatment, UHF, as well as alternating currents. The local massage will also give a good result.
Physiotherapy aims to reduce the severity of pain, eliminate inflammation, normalize metabolic processes in the affected joint and restore its normal function.
GREAT! It is important for the patient to monitor his diet and avoid strenuous physical exercise.
Forecast. Prophylaxis
With advanced disease, the prognosis is disappointing. Therefore, it is recommended that you consult a physician for advice if you experience even minor symptoms of arthritis.
People at risk (elderly, athletes, as well as overweight people) should follow the doctor's recommendations and follow the following rules:
- Eat right and control your weight. Follow a weight loss diet as needed.
- Reduce the load on the joints while playing sports, watch it constantly.
- Early treatment of infectious diseases, preventing their transition to the chronic stage.
- Get enough rest, avoid stressful situations if possible.
- Increase the protective functions of the body (you periodically take vitamins, temperament).
- Avoid hypothermia of the body, especially of the lower extremities.

















































